ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Changchun Yutai Optics Co., Ltd.
Home > Products > Prisms > Beamsplitters
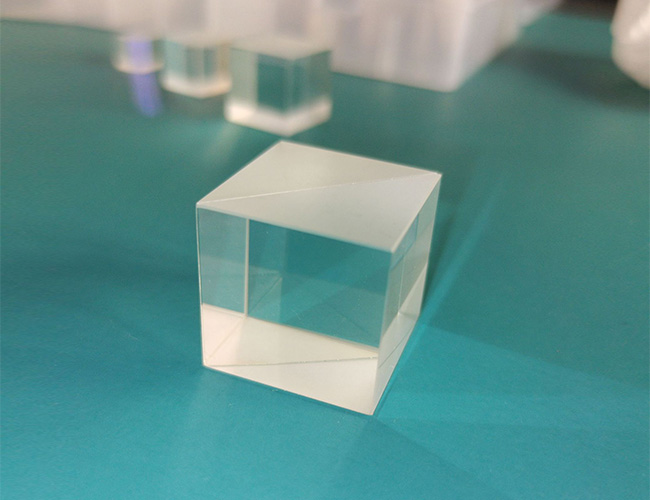
Polarizing Beamsplitter (PBS)
Function of Polarizing Beamsplitter (PBS): splits the incident light into two orthogonally polarized beams (usually S-polarized and P-polarized) according to the polarization state of the light.
Share this:
Operating Principle:
Using thin-film interference or birefringence effects (e.g., Wollaston prisms, Glen-Taylor prisms), incident light is decomposed into:
S polarized light (perpendicularly polarized, reflected light)
P polarized light (parallel polarization, transmitted light).
The splitting ratio is highly dependent on the state of polarization, e.g. 50:50 PBS will separate unpolarized light by state of polarization rather than equally by energy.
Characteristics:
Polarization dependent: the spectral separation effect is directly related to the polarization state of the incident light.
High extinction ratio: ideally, reflected light is purely S-polarized and transmitted light is purely P-polarized.
Application scenarios: laser systems, polarized imaging, optical isolators, quantum optics, and other fields that require polarization control.
Using thin-film interference or birefringence effects (e.g., Wollaston prisms, Glen-Taylor prisms), incident light is decomposed into:
S polarized light (perpendicularly polarized, reflected light)
P polarized light (parallel polarization, transmitted light).
The splitting ratio is highly dependent on the state of polarization, e.g. 50:50 PBS will separate unpolarized light by state of polarization rather than equally by energy.
Characteristics:
Polarization dependent: the spectral separation effect is directly related to the polarization state of the incident light.
High extinction ratio: ideally, reflected light is purely S-polarized and transmitted light is purely P-polarized.
Application scenarios: laser systems, polarized imaging, optical isolators, quantum optics, and other fields that require polarization control.
| Polarizing Beamsplitter (PBS) | |
| Material | BK7 or ZF |
| Dimension | 3×3mm-50×50mm |
| S/D | 60/40, 40/20 |
| Flatness | λ/4 - λ/10 |
| Transmission | Tp>95% |
| Reflection | Rs>99% |
| Extinction Ratio | 300:1, 1000:1 |
| Wavelength | VIS(400-700nm) |
| Application | diode,gas laser,solid-state laser |

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

