ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Changchun Yutai Optics Co., Ltd.
Home > Products > Prisms > Beamsplitters
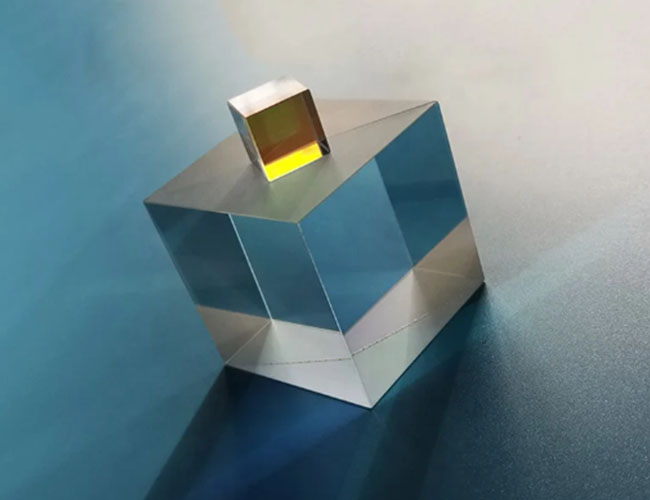
Optical N-SF11 Beamsplitters
Refractive index (nd): 1.784@587.6 nm 1.760@1064 nm Abbe number (vd): 25.7 (strong dispersion, need to pay attention to chromatic aberration). Transmission range: approx. 380 nm - 2500 nm (visible to near infrared). Density: 3.86 g/cm³ (heavy, need to consider mechanical support). Coefficient of thermal expansion: 8.2 x 10-⁶/°C (higher than BK7, less temperature stable).
Share this:
What are the advantages and disadvantages of SF11 beamsplitters?
Advantages of SF11 beamsplitters
High refractive index: enables smaller beam splitting angles or more compact optical path designs. Ideal for high angle incidence or scenarios requiring large angle beam splitting (e.g. laser resonant cavities).
Broadband beamsplitting: covers visible to near-infrared, suitable for multi-wavelength systems.
Coating compatibility: can be coated with Polarized Beamsplitters (PBS) or Non-Polarizing Beamsplitter (NPBS).
Disadvantages of SF11 beamsplitters
High dispersion: not suitable for broadband light source beamsplitting, prone to introducing chromatic aberration. Needs to be paired with a low dispersion material (e.g. fused silica) to form an achromatic prism.
Temperature sensitivity: high coefficient of thermal expansion, avoid use in environments with drastic temperature changes.
Cost and processing: more expensive than BK7 and more difficult to polish (soft glass scratches easily).
Advantages of SF11 beamsplitters
High refractive index: enables smaller beam splitting angles or more compact optical path designs. Ideal for high angle incidence or scenarios requiring large angle beam splitting (e.g. laser resonant cavities).
Broadband beamsplitting: covers visible to near-infrared, suitable for multi-wavelength systems.
Coating compatibility: can be coated with Polarized Beamsplitters (PBS) or Non-Polarizing Beamsplitter (NPBS).
Disadvantages of SF11 beamsplitters
High dispersion: not suitable for broadband light source beamsplitting, prone to introducing chromatic aberration. Needs to be paired with a low dispersion material (e.g. fused silica) to form an achromatic prism.
Temperature sensitivity: high coefficient of thermal expansion, avoid use in environments with drastic temperature changes.
Cost and processing: more expensive than BK7 and more difficult to polish (soft glass scratches easily).

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

