ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Changchun Yutai Optics Co., Ltd.
Home > Products > Prisms > Equilateral Prisms
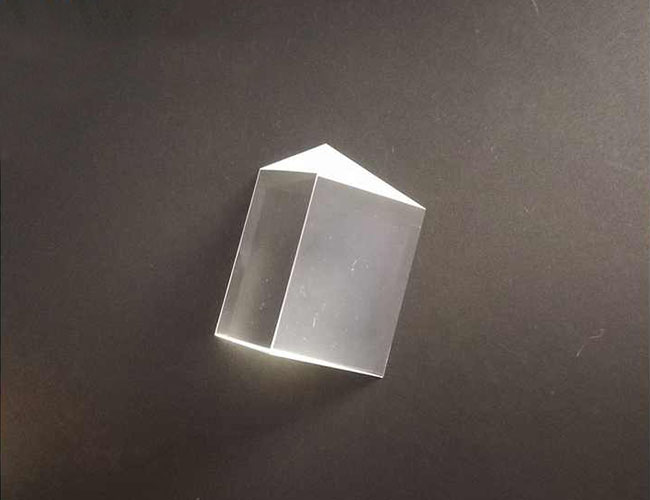

BK7 Optical Glass Equilateral Prism
An equilateral prism usually refers to an optical prism with an equilateral triangular cross-section, also known as an Equilateral Triangular Prism. These prisms are widely used in optical experiments and instruments.
Share this:
What are the advantages of BK7 (K9) equilateral prisms?
1. Cost-effective
Low cost: BK7 is a common optical glass, the raw material and processing cost is much lower than fused silica, suitable for projects with limited budget.
Easy to process: BK7 has moderate hardness (Mohs hardness 6-7) and is easy to cut, polish and coat, making it suitable for mass production.
2. Excellent optical transmittance
Outstanding performance in visible wavelength: high transmittance in the range of 350nm-2000nm (especially >90% in 400nm-1000nm), suitable for visible and near infrared applications (e.g. cameras, microscopes, laser systems).
Low bubbles and impurities: BK7 glass has high purity and few internal defects, reducing light scattering and energy loss.
3. Low dispersion (medium Abbe number)
Abbe number about 64.2: dispersion is lower than ordinary glass, but higher than fused silica (Abbe number 67), suitable for medium precision optical systems (e.g., imaging lenses, telescopes) that need to control chromatic aberration.
4. Stable mechanical and chemical properties
Environmental resistance: resistant to humidity and slight acid and alkali corrosion, suitable for laboratory or industrial environments.
Moderate coefficient of thermal expansion (7.1×10-⁶/°C): not as stable as fused silica, but reliable performance in the conventional temperature range (-30°C~70°C).
How do I choose the material for an equilateral prism?
BK7: general purpose optical systems, low cost experiments, imaging applications.
SF11: scenarios requiring strong dispersion or high refractive index (e.g. spectrometers).
Fused silica: UV wavelength or high laser damage threshold needs.
1. Cost-effective
Low cost: BK7 is a common optical glass, the raw material and processing cost is much lower than fused silica, suitable for projects with limited budget.
Easy to process: BK7 has moderate hardness (Mohs hardness 6-7) and is easy to cut, polish and coat, making it suitable for mass production.
2. Excellent optical transmittance
Outstanding performance in visible wavelength: high transmittance in the range of 350nm-2000nm (especially >90% in 400nm-1000nm), suitable for visible and near infrared applications (e.g. cameras, microscopes, laser systems).
Low bubbles and impurities: BK7 glass has high purity and few internal defects, reducing light scattering and energy loss.
3. Low dispersion (medium Abbe number)
Abbe number about 64.2: dispersion is lower than ordinary glass, but higher than fused silica (Abbe number 67), suitable for medium precision optical systems (e.g., imaging lenses, telescopes) that need to control chromatic aberration.
4. Stable mechanical and chemical properties
Environmental resistance: resistant to humidity and slight acid and alkali corrosion, suitable for laboratory or industrial environments.
Moderate coefficient of thermal expansion (7.1×10-⁶/°C): not as stable as fused silica, but reliable performance in the conventional temperature range (-30°C~70°C).
How do I choose the material for an equilateral prism?
BK7: general purpose optical systems, low cost experiments, imaging applications.
SF11: scenarios requiring strong dispersion or high refractive index (e.g. spectrometers).
Fused silica: UV wavelength or high laser damage threshold needs.

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

