ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
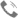 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Changchun Yutai Optics Co., Ltd.
Home > Products > Filters > Neutral Filters
Reflective Neutral Density (ND) Filters
The reflective ND filter attenuates light intensity by reflecting (rather than absorbing) a portion of the incident light while maintaining spectral neutrality. It is more suitable for high power lasers or applications where thermal effects need to be minimized than absorptive ND filters.
Share this:
| Comparison of Absorptive ND Filter and Reflective ND Filter | ||
| Feature | Reflective ND Filter | Absorptive ND Filter |
| Attenuation Mechanism | Reflective | Absorptive |
| Thermal Effect | Low (no heat from reflected light) | High (absorption of light into heat) |
| Damage Threshold | Higher (for high power lasers) | Lower (may be damaged by overheating) |
| Spectral Neutrality | Excellent (dependent on coating process) | Good (adulterated materials may have slight color deviation) |
| Angular Sensitivity | Higher (large angle of incidence may change OD value) | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
What are the considerations for choosing a reflective neutral density filter?
Power Tolerance:
Confirmation of laser wavelength and power density (e.g. CO₂ lasers require ZnSe substrates).
Dielectric ND filters typically withstand >1 kW/cm² (pulsed lasers require additional consideration of peak power).
Stray Light Treatment:
Reflected light needs to be directed in a harmless direction (e.g. beam traps).
Spectral Range:
Ultraviolet (UV) or infrared (IR) bands require special coatings (e.g. UV fused silica substrate).

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

