ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Changchun Yutai Optics Co., Ltd.
Home > Products > Filters > IR Filters
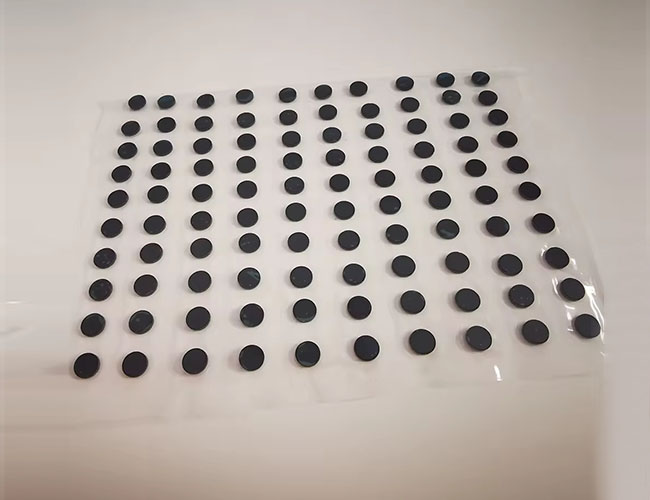

Optical IR Bandpass Filters
An infrared bandpass filter is an optical element that selectively transmits a specific infrared wavelength while blocking light outside of that wavelength (including UV, visible and other non-targeted infrared light).
Share this:
The working principle of IR bandpass filters
Passband: the centre wavelength (e.g. 3.4μm) and full width at half maximum (e.g. ±0.2 μm) allowed to be transmitted, usually achieved by multilayer dielectric coatings or interference structures.
Blocking Range: light outside the passband is strongly attenuated (OD>4, i.e. transmittance<0.01%).
What are the key characteristics of IR bandpass filters?
Key Characteristics
CWL: the wavelength corresponding to the peak of the passband.
FWHM: half height full width, divided into narrow band (e.g. 10 nm) and wide band (e.g. 500 nm).
Transmittance: usually T>80% in the passband, up to T>90% for high-end filters.
Blocking: very low transmittance outside the passband (e.g., OD>6 in the UV-VIS, OD>4 in the IR).
Angular Sensitivity: increased angle of incidence leads to a blue shift in the passband (collimation needs to be considered).
Passband: the centre wavelength (e.g. 3.4μm) and full width at half maximum (e.g. ±0.2 μm) allowed to be transmitted, usually achieved by multilayer dielectric coatings or interference structures.
Blocking Range: light outside the passband is strongly attenuated (OD>4, i.e. transmittance<0.01%).
What are the key characteristics of IR bandpass filters?
Key Characteristics
CWL: the wavelength corresponding to the peak of the passband.
FWHM: half height full width, divided into narrow band (e.g. 10 nm) and wide band (e.g. 500 nm).
Transmittance: usually T>80% in the passband, up to T>90% for high-end filters.
Blocking: very low transmittance outside the passband (e.g., OD>6 in the UV-VIS, OD>4 in the IR).
Angular Sensitivity: increased angle of incidence leads to a blue shift in the passband (collimation needs to be considered).

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

