ISO9001 Certified Professional Manufacturer & Supplier of Optics
+86-0431-87911611 admin@ytoptics.com
Contact us
-
 Email: admin@ytoptics.com
Email: admin@ytoptics.com
-
 Tel:86-0431-87911611
Tel:86-0431-87911611
-
 Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Add: 2# Automotive Innovation
Jilin Province, China
Changchun Yutai Optics Co., Ltd.
Home > Products > Filters > Longpass Filters
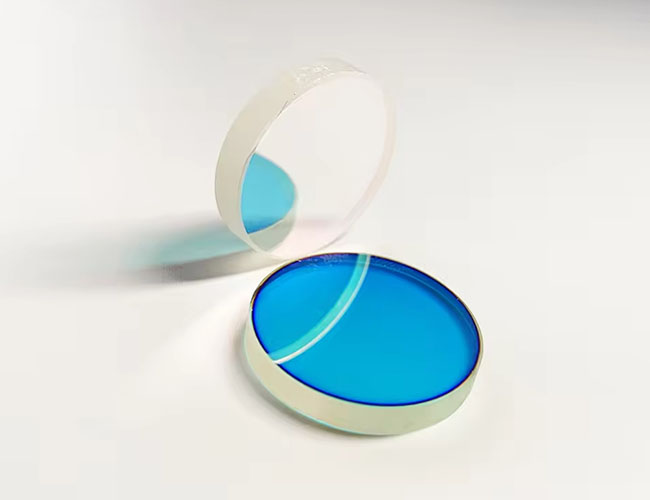

Optical Cold Mirrors
Cold mirror is a special optically coated mirror that reflects visible light while efficiently transmitting infrared thermal radiation (typically >700nm). This selective spectral control makes it ideal for scenarios requiring precise illumination and thermal management.
Share this:
Principle of operation of cold mirrors
Dielectric Interference Coating: through the precise stacking of multiple layers of TiO₂/SiO₂ and other thin films, the following can be realized: high reflectance of visible light (R>95%@400-700nm), highly efficient transmittance of infrared light (T>80%@700-2500nm).
Heat Dissipation: the infrared energy penetrates through the mirrors directly, which avoids the accumulation of heat from the light source (e.g., halogen lamps, LEDs).
What are the applications of cold mirrors?
Projection Systems: reducing thermal stress on LCD/DLP projectors to extend chip life.
Microscope Lighting: reducing thermal damage to samples and improving observation clarity.
Stage Lighting: reducing equipment temperature while maintaining high brightness output.
Medical Equipment: heat management for surgical shadowless lamps.
Dielectric Interference Coating: through the precise stacking of multiple layers of TiO₂/SiO₂ and other thin films, the following can be realized: high reflectance of visible light (R>95%@400-700nm), highly efficient transmittance of infrared light (T>80%@700-2500nm).
Heat Dissipation: the infrared energy penetrates through the mirrors directly, which avoids the accumulation of heat from the light source (e.g., halogen lamps, LEDs).
What are the applications of cold mirrors?
Projection Systems: reducing thermal stress on LCD/DLP projectors to extend chip life.
Microscope Lighting: reducing thermal damage to samples and improving observation clarity.
Stage Lighting: reducing equipment temperature while maintaining high brightness output.
Medical Equipment: heat management for surgical shadowless lamps.

TALK TO US 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611
Call us now!
 86-0431-87911611
86-0431-87911611Call us now!
ONLINE CHAT
 2433808388
2433808388

